Bingung mau olah data laporan dengan tabel microsoft excel yang datanya banyak dan jenis laporan yang harus dibuat juga banyak?. Anda dapat Membuat Pivot Tabel Microsoft Excel untuk mengurai laporan berdasarkan data tabel microsoft excel.
Untuk mempermudah penjelasan berikut contoh kasus, Coba perhatikan tabel data microsoft excel di bawah ini : 
Pivot Tabel merupakan fitur canggih dari Microsoft Excel yang memungkinkan anda untuk membuat pelaporan analisa data sekaligus melakukan manipulasi data yang cepat. Mengunakan Pivot tabel dalam Microsoft Excel dapat meringkas data laporan yang lebih simpel dan mudah dimengerti.
Memulai Menggunakan Pivot Tabel Pada Microsoft Excel
Untuk membuat Pivot Tabel pada Microsoft Excel, kita harus memiliki tabel sumber data awal yang akan menentukan nilai pada tabel pivot. Mempersiapkan tabel sumber data adalah hal yang terpenting dalam memulai menggunakan Pivot Tabel. Tabel Sumber data awal harus memiliki nama kolom yang lengkap dan tidak boleh kosong (Seperti contoh gambar di atas). Usahakan agar tabel kolom tidak digabung atau merged cell. Tabel sumber data adalah hal yang terpenting dalam menentukan nilai pivot tabel yang benar sehingga menghasilkan jenis laporan yang kita inginkan.
Cara Membuat Pivot Tabel Microsoft Excel
Setelah meyiapkan tabel sumber data utama, yang perlu kita tetapkan adalah jenis laporan yang ingin kita hasilkan dari data sumber utama. Seperti contoh kasus gambar di atas, kita menginginkan agar pada pivot tabel menghasilkan data belanja barang berdasarkan Suplier. Untuk membuatnya mari kita simak cara membuat Pivot Tabel di Bawah ini :
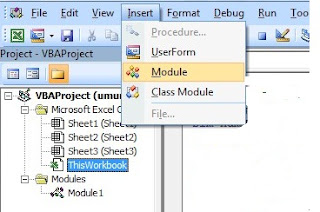
- Pilih Menu Insert lalu Klik pada Pivot Table

- Lalu tentukan range untuk data sumber pada form Create Pivot Table di bawah ini

- Setelah menentukan sumber data awal untuk pelaporan pivot table, anda dapat menentukan jenis laporan yang anda inginkan. Kembali kepada kasus yang telah kita bahas, berdasarkan tabel sumber data, kita akan membuat pelaporan belanja barang berdasarkan Supplier, maka data filter yang akan kita gunakan adalah Supplier. Untuk lebih jelas lagi perhatikan gambar di bawah ini :
 Keterangan Gambar :
Keterangan Gambar :- Merupakan kumpulan Field atau kolom pada sumber data awal.
- Field atau kolom SUPPLIER menjadi Report Filter karena sesuai kasus di atas, kita akan menjadikan SUPPLIER sebagai dasar pelaporan. Untuk mengisi Report Filter, Klik field SUPPLIER (no.1) lalu drag ke kolom Report Filter.
- Untuk Row Labels kita isi dengan Nama Barang. Cara mengisi Row Labels sama dengan mengisi Report Filter, yaitu dengan meng-klik Field Nama Barang pada kolom no.1 lalu drag ke kolom Row Labels
- Untuk Colom labels kita kosongkan (Sesuai dengan kebutuhan pelaporan yg akan kita buat)
- Kolom ∑ Values kita dapatkan dengan klik kanan pada Field HARGA (no.1) lalu pilih add to ∑ Values. Untuk lebih jelas anda dapat melihat gambar di bawah ini
 Maka secara otomatis kolom ∑ Values akan terisi dengan sum of Harga.
Maka secara otomatis kolom ∑ Values akan terisi dengan sum of Harga.
Setelah semua langkah dan cara Membuat Pivot Tabel Microsoft Excel yang anda buat di atas telah benar maka hasil dari Pivot tabel akan tampak seperti gambar di bawah ini :

Nah mudah sekali bukan untuk menghasilkan laporan dengan cara Membuat Pivot Tabel Microsoft Excel ?,. hal yang perlu anda perhatikan adalah sumber data awal, lalu perencanaan bentuk laporan yang sesuai dengan sumber data awal.
Demikian penjelasan dan Tutorial Cara Membuat Laporan Pivot Tabel pada Microsoft Excel semoga bermanfaat bagi anda.